A rare diamond is forever, and also worth a fortune. The famous line “A diamond is forever” was from a De Beers jeweler advertisement.
The line became a cultural phenomenon, leading to one of the beloved James Bond novel titles, “Diamonds Are Forever,” and countless references over the decades.
Diamonds have captured the hearts and minds of people for thousands of years.
Since 1477, when eighteen-year-old Archduke Maximillian gave his bride, Mary of Burgundy, the first-ever diamond engagement ring, the tradition has continued and exploded the diamond industry to a $90 billion global market.
Rare Diamond Popularity
Engagement rings helped launch the diamond industry to enormous size, beginning with that first gift over 500 years ago.
They are coveted, loved, idolized, and a status symbol like none other. Rare diamonds have also appreciated over the years, just like any other desirable item.
Large diamonds, small diamonds, and everything in between. From rough stones to polished gems and amazing diamond ring creations. Royalty to celebrities and private collectors, rare and valuable diamonds are a fascinating topic.
Let’s look at some of the most valuable, rare, and famous diamonds in the world. But first, what makes a diamond rare and valuable?

What Makes a Rare Diamond Valuable?
There are few things as gorgeous to gaze upon as a high-quality polished diamond. Natural diamonds are beautiful too. They’re also not that easy to mine.
The amount of work and infrastructure it takes to mine these precious stones is staggering.
Furthermore, only about 30% of diamonds mined meet the standard, making suitable diamonds relatively rare. However, they are also practical and valuable due to their hardness and are used in various tools and machines.
Not all diamonds are created equally, though. The value and rarity are based on one or all of the four Cs – Clarity, Color, Cut, and Carat Weight.
These are classification factors, and if specific characteristics are scarce in one or more categories, the diamond becomes more expensive due to its rarity. The rarest diamonds are worth millions.

Let’s take a closer look at the four Cs.
Rare Diamond Color
The color of a diamond is significant. Different colors form for various reasons, from the formation of the nitrogen atoms to the geographical location and the age of the diamond.
Each natural color produces a perfect storm of minerals, atmospheric pressures and temperatures, time, gasses, and elements.
There are quite a few subcategories within the color category that determine the classification and value.
- Entry-Level Pricing – Gray, Brown, and Fancy Yellow Diamonds
- Mid-Range Pricing – Intense and Vivid Yellow Diamonds and Orange Diamonds
- High-End Pricing – Pink, Purple, Violet, Green, and Blue Diamonds
- Prestige Pricing – the rarest diamond color: Red

Fancy color diamonds are the rarest and most valuable, coming in almost any color imaginable. Besides the actual color, there is also a rating system for the level of color saturation, in other words, the intensity of the color of the diamond.
This system adds another layer of value to rare diamonds, from least desirable to most desirable.
- Faint
- Very Light
- Light
- Fancy Light
- Fancy
- Fancy Intense
- Fancy Vivid
- Fancy Deep
- Fancy Dark
Rare Diamond Clarity
Clarity is another metric for determining the value of a diamond, and the clarity largely depends on two factors – Inclusions and blemishes.
The more minor inclusions and blemishes present, the higher the clarity and the more valuable the diamond.
- Inclusions – These are the interior features of a diamond, as opposed to the surface features, although sometimes, inclusions can break to the surface of the diamond. Things like mineral crystals and other tiny diamonds can often forge and grow with the diamond, which would be considered inclusions.
- Blemishes – Imperfections on the surface of the diamond are referred to as blemishes. These include things like scratches, nicks, and scrapes.
While the presence of inclusions and blemishes can lower the value of a diamond, they can also be helpful in a couple of ways.
Rare Diamond Clarity for Detecting Fakes
First, they help to decipher genuine precious diamonds from imitations. Some synthetic diamonds are exceptionally well made. Diamonds with inclusions and blemishes are easier to tell apart from fakes than flawless diamonds are.
Secondly, the inclusions and blemishes are always unique to each diamond. Therefore, it helps identify individual stones and helps scientists analyze the processes that created the diamond.
Clarity categories include:
- Flawless (FL) – No inclusions or blemishes are visible
- Internally Flawless (IF) – No inclusions and only slight blemishes
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) – Inclusions are difficult to see
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2) – Inclusions are minor and range from difficult to somewhat easy to see
- Slightly Included (SI1 and SI2) – Inclusions are noticeable
- Included (I1, I2, and I3) – Inclusions are apparent and may affect transparency and brilliance
Rare Diamond Cut
The cut of the stone is a more all-encompassing term than the others in that it takes several different factors into account. Facets, symmetry, dimensions (size), and reflective qualities are considered here.
Rare Diamond Cuts
Marquise
Oval
Cushion
Trilliant
Royal Asscher Cut
Radiant
Round Brilliant
Emerald Cut
Princess Cut Diamond
Heart
Pear
Baguette
There are several other, even more rare diamond cuts. For example, the Eighty-Eight Cut, the Lily cut, Bead Cut, PrincessPlus Cut, and the Crisscut.
As such, cut is probably the most significant factor determining value. The rarest cuts are the most valuable as always, and size often plays a role.
Some of the factors affecting the cut include:
Natural attributes
- Brightness – All the light reflected
- Fire – The dispersion of light into the colors of the spectrum
- Scintillation – the flickering of light and how it dances when the diamond is moved around
Design and craftsmanship
- Weight ratio
- Durability
- Polish
- Symmetry
There are many different systems for measuring the cut, but generally, the factors measured remain the same.
The cut is also quite often used interchangeably with shape. While the shape is a factor that affects cut, they are not the same, as the diamond cut incorporates multiple factors.
Rare Diamond Cut Combinations
Another factor to consider regarding the cut is the immeasurable combinations of possibilities. Quite often, the look and feel of a rare diamond is subjective and depend on personal preference.
That being said, one must apply standards to determine value, and these standards remain objective.
Lastly, most diamond jewelry uses a round shape, and anything other than round is known as ”fancy”. This includes hearts, marquise, pear, oval, princess cut, triangles, and many different fancy shapes exist.
Shape largely depends on the original form of the rough diamond and the popularity of certain shapes in specific markets.
Rare Diamond Carat Weight
Like most products, diamonds are also valued based on their weight. Metric carats are used here, with one carat equal to 0.2 grams.
Each carat is divided into 100 points; for example, a 50-point diamond will weigh 0.50 carats.
Now that we understand what features and characteristics make diamonds valuable, it’s time to check out the most valuable diamonds in the world! We’ll begin with diamond colors.
The Most Valuable Rare Diamond Colors
As mentioned, color profoundly affects diamond value – Let’s take a closer look at several diamonds featuring various color grading scales.
Red Diamonds
When it comes to rare and expensive, red is the color. The fancy red diamond has dominated auction house prices for years.
Many of the most valuable red diamonds come from the Argyle Diamond Mine in Western Australia.
- Red diamonds are scarce – There are only around 30 natural fancy red diamonds in the world.
- They are costly, too, with an average price tag of around $1 million per carat.
- Unlike other colored diamonds, their hue is because they are pure carbon. Red fancy diamonds exhibit the same mineral properties as colorless diamonds.
The most famous red diamonds are The Moussaiff Red and The Hancock Red.
The Moussaieff Red Diamond
The largest red diamond in the world comes in at 5.11 carats.
Previously known as The Shield Diamond was renamed in 2001 when Israeli diamond and jewelry dealer Shlomo Moussaieff purchased it for around $8 million.
The Hancock Red Diamond
Formerly known as the Halphen Red Diamond, this 0.95-carat Fancy Purple-Red Brazilian diamond is worth around $1 million per carat.
It is famous for being the first-ever gem-quality stone sold at auction in 1987 for $880,000.
Blue Diamonds
Blue diamonds rated Type IIb Fancy have grading scales ranging from Faint Blue to Fancy Dark Blue. Fancy intense blue and fancy deep blue diamonds are the most valuable.
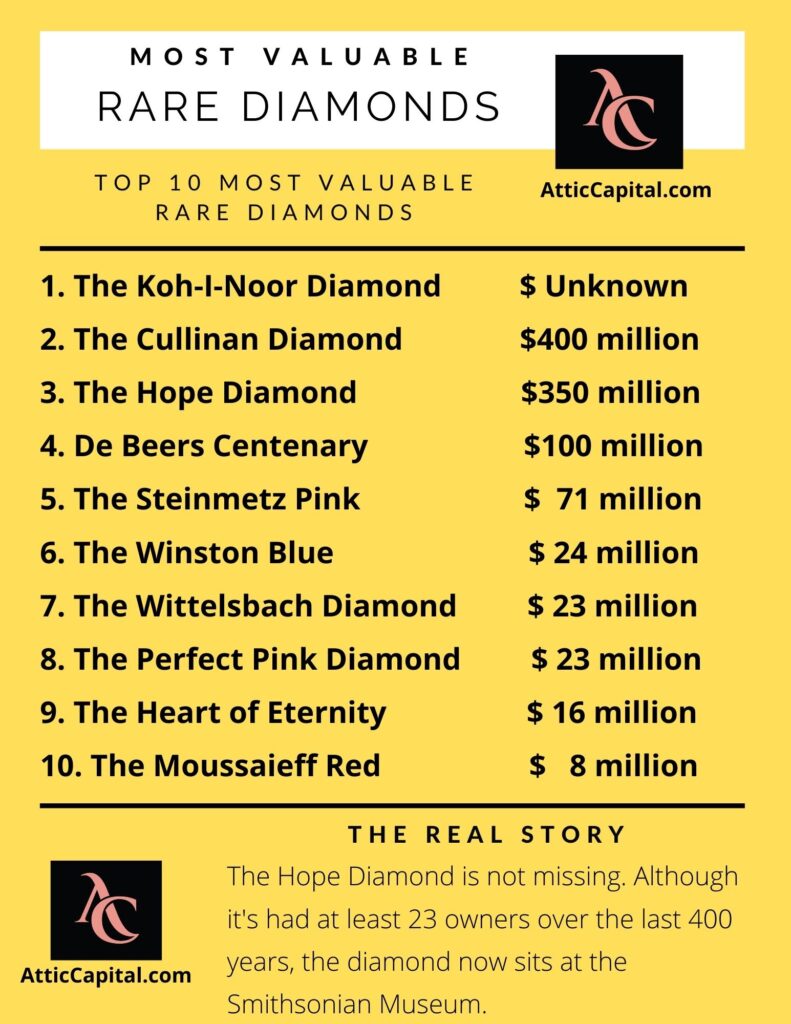
The Hope Diamond
This 45.52-carat Fancy Dark Gray-Blue is the most valuable blue diamond globally. The beautiful stone is estimated to be valued at $200 to $350 million.
The Blue Moon Diamond
12.03 carats and classified as a Vivid IF Blue Diamond, this near-flawless diamond was purchased for $48.5 million by Hong Kong billionaire Joseph Lau as a gift for his seven-year-old daughter at a Sothebys auction.
Yellow Diamonds
Yellow is the most common diamond color, and they get their color from nitrogen. So canary yellow is the most sought-after yellow diamond, and because it’s the most common color, it is also one of the cheapest at around $6,500 to $8,000 per carat.
Pink Diamonds
They are pure and get their color from plastic deformation like red diamonds. Depending on the cut, they can range between $10,000 and $700,000 per carat.
So, how rare is a Pink Diamond? That depends, but there are a couple of extremely rare types.
The Graff Pink
A 14-carat Fancy Intense pink diamond, this beauty sold just under $20 million in 2010.
The Steinmetz Pink
Renamed The Pink Star and The Pink Dream by different buyers, this is the largest Vivid Pink diamond ever, weighing 59.6 carats. It once sold for over $83 million and is one of the top 5 most valuable diamonds ever.
Orange Diamonds
The incorporation of nitrogen mineral atoms gives these diamonds their orange hue. Interestingly, orange diamonds are rare, especially pure orange diamonds without secondary colors.
The Pumpkin Orange Diamond
The 5.54-carat Fancy Vivid orange cushion-shaped diamond was found in South Africa and is estimated at over $3 million.
Green Diamonds
Green diamonds are scarce and get their color from irradiation. As a result, the green hue is often only on the surface, but pure green diamonds with the full color going all the way through are very rare and expensive.
The Dresden Green Diamond
It is a flawless 40.70 Pear-Shaped green diamond dating back to 1722. It is housed at the Albertinum Museum in Dresden.
Black Diamond, Brown Diamond, and White Diamonds
The more common and, therefore, cheaper diamonds are black, brown, and white. Although, there are certain exceptions, such as Type IIA white diamonds, which can be very valuable.
Carbonado diamonds, also known as black diamonds, date back 2.6 to 3.8 billion years.
Traces of hydrogen and nitrogen are also found in interstellar space, making black diamonds very rare and desirable. Black diamonds are worth about $3,000 per carat.
Most Valuable Rare Diamonds in the World
What are the world’s most rare and expensive diamonds?
1. The Koh-I-Noor Diamond – Value Unknown
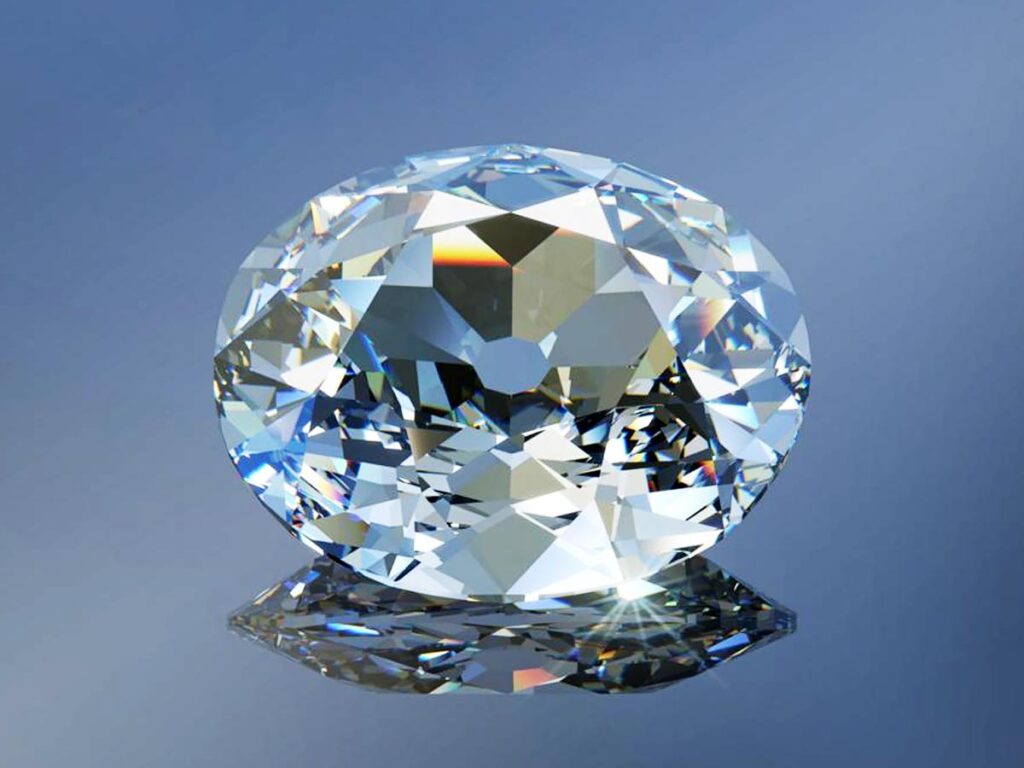

Mined in India in the 1300s, the Koh-I-Noor is the most valuable and most expensive diamond in the world. There’s just one small problem; it’s such a stunning diamond there’s no way to value it.
Weighing 105.6 ct, the diamond has much controversy behind it. Some say the gem was stolen from India by Britain in 1850.
A few years later, Prince Albert cut the stone down from 186ct to 105.6ct to show its sparkle and brilliance. The diamond is also known as the Diamond of Babur or the Mountain of Light.
2. The Cullinan Diamond – $400 million
- 621 grams – The largest diamond in the world. Found in Botswana, South Africa in 1905.
- The 530-carat Star of Africa was cut from it

3. The Hope Diamond – $350 million

4. De Beers Centenary Diamond – $100 million
- A flawless, colorless diamond
- 273.85 carats
5. The Steinmetz Pink Diamond – $71 million

6. The Blue Moon of Josephine – $48 million
The fancy vivid blue 12.03 carat diamond sold at a Sotheby’s auction in Geneva in 2015. The diamond was found at the Cullinan mine in South Africa in 2014.
7. De Beers Millennium Jewel 4 – $32 million
8. The Zoe Diamond – $32 million
9. The Winston Blue – $24 million
Purchased by a private collector during a Christie’s auction in 2014.
10. The Wittelsbach-Graff Diamond – $23.5 million
The deep blue flawless diamond was pulled from the Kollur mines of Andhara Pradesh in India. The 31.06 carat diamond was originally owned by Spain’s King Philip IV.
11. The Perfect Pink Diamond – $23 million
12. The Heart of Eternity – $16 million
13. The Moussaieff Red Diamond – $8 million

14. The Farnese Blue – $6 million
Evaluating Rare Diamond Quality
As you can imagine, buying and selling rare diamonds is a treacherous endeavor. Luckily, the industry is at least attempting to enforce standards and certifications for analyzing and grading rare diamonds.
The Gemological Institute of America was established in 1931 by Robert M. Shipley as the world’s leading authority on colored stones, diamonds, and pearls.
The GIA is a nonprofit institute providing education, standards, and knowledge in jewelry and gems. During the 1940s, the GIA created the “4Cs” and the “International Diamond Grading System.”
Besides the four Cs, two significant categories determine the value of diamonds:
TYPE I DIAMONDS
- Approximately 98% of all gem diamonds fall into the type IaA and type IAB
- IaA have paired nitrogen atoms and are found mainly in the Cape Province of South Africa
- IaB have clustered nitrogen atoms are located in Buffalo Hills, Namibia, and Eurasia
TYPE II DIAMONDS
- Rarer and more valuable diamonds are classified as type II
- Type IIa diamonds are the most chemically pure diamond available and has no measurable nitrogen or boron impurities
- Type IIb diamonds contain no nitrogen but does contain boron
What’s Rarer Than a Diamond?
While rare diamonds get plenty of attention, it’s important to note there are several gemstones rarer than diamonds.
A few extremely rare gemstones are Tanzanite, Kashmir Sapphire, Ammolite, Alexandrite, and Jadeite.
Where to sell my Rare Diamond?
Auction House – A few of the most popular auction houses featuring rare diamonds are Sotheby’s, Bonhams, Christie’s, Heritage, Richie’s, and Weschler’s.
Online Diamond Buyer – There are hundreds, if not thousands of online rare diamond buyers. Choose carefully.
eBay or Craigslist – eBay or Craigslist is another place to list your rare diamond. Know the value of your diamond before you list, and don’t settle for low-ball offers.
Consignment Shop – A reputable jeweler or consignment shop can be a great way to sell your rare diamond. It might take longer to realize a sale, but if you find the right shop, it will be worth it.
Rare and valuable diamonds are genuinely fascinating, and they are also great to invest in. Diamonds seldom lose their value over long periods of time.
Unlike the currently volatile markets, they have the possibility to make a solid and stable investment for many years.
What’s the Biggest Rare Diamond Heist in History?
It only takes a few minutes of thinking about rare diamonds before you ask yourself, “what’s the biggest diamond heist ever?”
Well, there’s one heist known as the, “heist of the century,” and it involved over $100 million worth of diamonds, gold, silver, and jewelry.
The heist occurred in the Antwerp diamond district in Belgium, and included over 18 months of planning and surveillance by the mastermind thieves.
It’s an amazing tale of preparation, deception, and a vault with 100 million combination possibilities. Although the mastermind behind the heist, Leonardo Notarbartolo, was caught, much of the stolen loot was never recovered.

R.J. Bachman
Attic Capital – Writer, Editor, and Lifelong Collector
I would love to connect with you, so don’t hesitate to reach out and let me know more about your passion for collecting.
